How to Use Our BMI Calculator
Getting your BMI result is quick and easy. Just follow these simple steps for an accurate reading:
tep 1: Enter Your Basic Details
- Age: Enter your current age in years. This calculator is suitable for adults aged 18 and above.
- Gender: Select whether you are Male or Female. This helps in providing a more contextual result.
Step 2: Provide Your Height
- Enter your accurate height in centimeters (cm). For best results, measure your height without shoes.
Step 3: Enter Your Weight
- Select Unit: First, choose your preferred weight unit, either Kilograms (KG) or Pounds (Lb).
- Enter Value: Once the unit is selected, enter your current weight in the box.
Step 4: Calculate and View Your Result
- Click the large blue “Calculate BMI” button.
- Instantly, the screen will display your result, showing:
- Your exact BMI value.
- Your weight category (e.g., Normal Weight, Overweight).
- A colored progress bar to help you visualize your status.
- A helpful expert tip based on your category.
Important Note: This calculator is an informational tool for adults. For children and teenagers, BMI is calculated differently and should always be assessed by a healthcare professional.
Understanding Your BMI: (The Official WHO Classification)
Wondering what your BMI means for your health? Your Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple yet powerful way to check if your weight is in a healthy range. Based on guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO), your BMI result can help you understand your risk of health issues like diabetes, heart disease, and more.
Use our free BMI calculator to find out your BMI instantly.
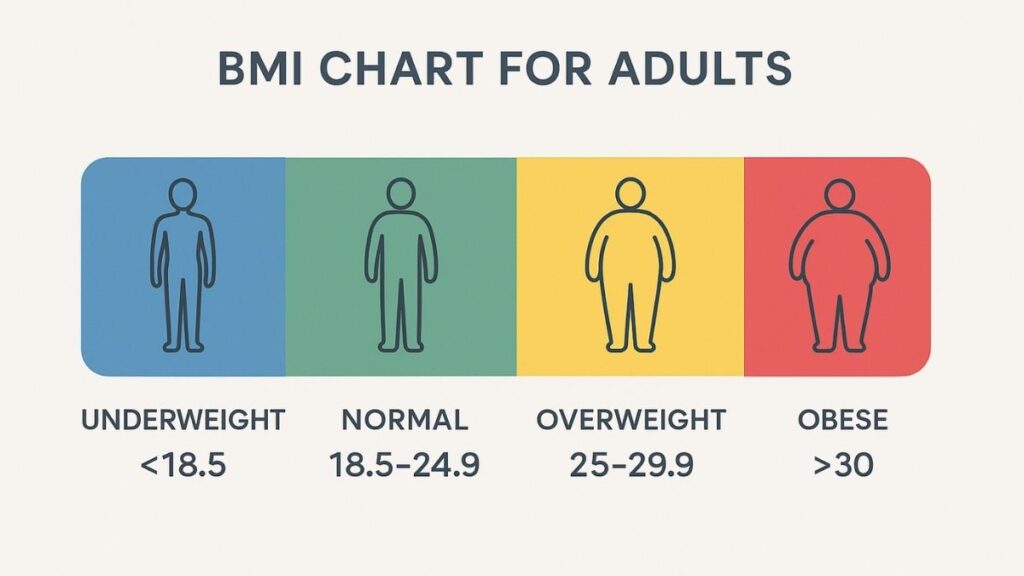
| Classification | BMI Range | Associated Health Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 18.5 | Low (but risk of other clinical problems increased) |
| Normal range | 18.5 – 24.9 | Average / Healthy |
| Overweight (Pre-obese) | 25.0 – 29.9 | Increased |
| Obese Class I | 30.0 – 34.9 | Moderate |
| Obese Class II | 35.0 – 39.9 | Severe |
| Obese Class III | 40.0 and Above | Very Severe |
Health Consequences of an Unhealthy BMI
According to WHO, being outside the normal BMI range is a major risk factor for several chronic diseases. The health risks increase as the BMI value moves further away from the normal range.
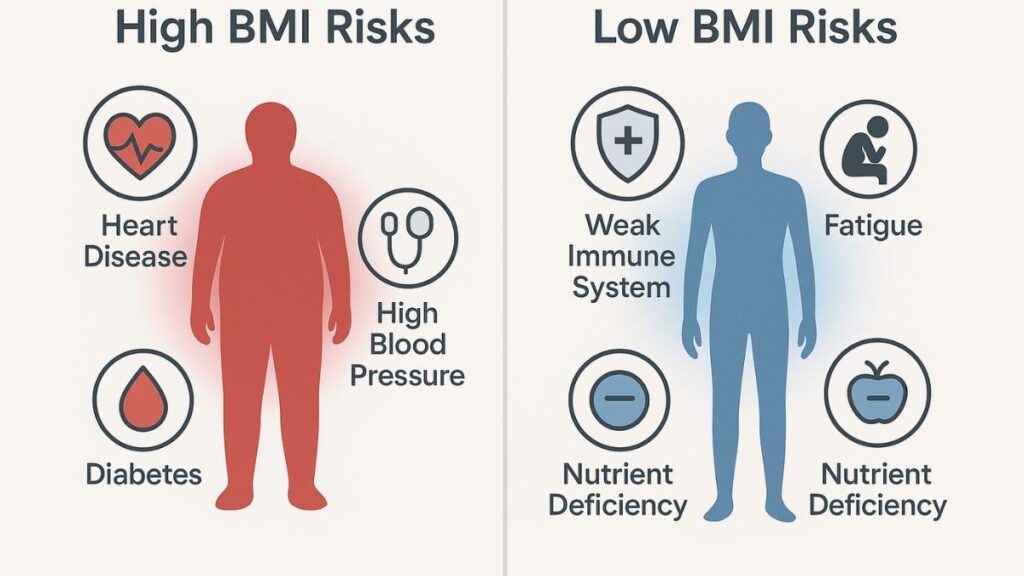
Major Health Risks Associated with High BMI (Overweight & Obesity)
- Type 2 Diabetes: The risk of developing NIDDM (Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus) is greatly increased.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Includes a higher risk of Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), hypertension (high blood pressure), and stroke.
- Certain Types of Cancer: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of endometrial, breast (postmenopausal), colon, and other cancers.
- Gallbladder Disease: The risk of developing gallstones is three to four times higher in obese individuals.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Conditions like osteoarthritis (especially of the knees) and gout are more common.
- Respiratory Problems: Includes breathlessness and a significantly higher risk of sleep apnea.
Risks Associated with Low BMI (Underweight)
- Increased risk of infectious diseases due to a weakened immune system.
- Reduced work capacity and higher chances of fatigue.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Can lead to conditions like anemia and osteoporosis.
- Problems with thermoregulation (maintaining body temperature).
WHO on the Limitations of BMI [Important]
While BMI is a very useful population-level measure, the WHO acknowledges that it may not be perfectly accurate for every individual. It is a crude index and does not distinguish between weight from muscle and weight from fat.
- Athletes and Bodybuilders: May have a high BMI due to high muscle mass, not excess fat.
- Ethnic Differences: The relationship between BMI, body fat percentage, and health risk can vary across different ethnic populations.
- Pregnant Women: BMI is not used to assess the health of pregnant women.
- The Elderly: Age-related loss of muscle can affect BMI accuracy.
A Practical Approach to Achieving a Healthy BMI
The WHO emphasizes that preventing obesity is more effective than treating it. Small, sustainable lifestyle changes are key.
1. Focus on a Healthy Diet
- Reduce High-Fat, Energy-Dense Foods: Limit consumption of processed foods, fast foods, and sugary drinks.
- Increase Complex Carbohydrates and Fiber: Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. These foods help in controlling energy intake.
- Balanced Meals: Ensure your meals are nutritionally balanced, rather than just focusing on calories.
2. Increase Daily Physical Activity
- Reduce Sedentary Time: The time spent watching TV, using a computer, or sitting for long periods is a major factor in weight gain.
- Incorporate Daily Activity: Aim for at least 30-60 minutes of moderate activity like brisk walking, cycling, or gardening on most days.
- Make Activity a Part of Life: Use stairs instead of elevators, walk for short journeys. The goal is an active lifestyle, not just occasional exercise.
A Man’s Guide to BMI
Men and women have different body compositions. Typically, men have more muscle mass and less body fat than women of the same height and weight. While our BMI calculator provides an accurate general reading, it’s important for men to understand these differences.
Understanding Body Composition and BMI for Men
- Muscle vs. Fat: A standard BMI calculation doesn’t differentiate between muscle and fat. If you are an athlete or have a very muscular build, your BMI might fall into the ‘Overweight’ category even if you have a healthy level of body fat.
- Abdominal Fat (Visceral Fat): Men are more prone to storing fat around the abdomen (a “beer belly”). This type of fat, known as visceral fat, is a significant risk factor for heart disease and type 2 diabetes, even if the overall BMI is only slightly high.
- Age and Metabolism: As men age, metabolism naturally slows down, and muscle mass tends to decrease, which can lead to weight gain.
A Woman’s Guide to BMI
A woman’s body composition and health considerations are unique. Hormonal changes throughout life, from puberty to menopause, can significantly impact body weight, fat storage, and BMI.
Special Health Considerations for Women
- Hormonal Impact: Women naturally have a higher percentage of body fat than men, which is essential for reproductive health. Hormonal fluctuations, especially during menopause, can lead to weight gain, particularly around the midsection.
- Pregnancy and BMI: Important: This calculator should not be used during pregnancy. Weight gain is a natural and necessary part of a healthy pregnancy, and BMI values are not applicable. Always consult a doctor for guidance on healthy pregnancy weight.
- Bone Health: A very low BMI (underweight) can be a risk factor for osteoporosis (weak bones), especially after menopause.
Common health risks for women associated with a high BMI include:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Increased risk of breast and endometrial cancer after menopause
- Gallbladder issues.
A Parent’s Guide to BMI in Children and Teenagers
Crucial Information: A standard adult BMI calculator is NOT suitable for children or teenagers (under 18). Children are still growing, and their body composition changes rapidly. A child’s BMI is calculated and interpreted differently, using age- and sex-specific percentile charts.

How is a Child’s BMI Measured?
A child’s BMI is plotted on a growth chart to get a percentile ranking. This percentile indicates how their BMI compares to other children of the same age and sex. This should always be done by a pediatrician.
| Percentile Range | Weight Status Category |
|---|---|
| Below 5th percentile | Underweight |
| 5th to < 85th percentile | Healthy Weight |
| 85th to < 95th percentile | Overweight |
| Equal to or > 95th percentile | Obesity |
For an accurate assessment of your child’s weight, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. You can learn more about this at the official CDC website.
Disclaimer:
Important Notice: This tool is for informational purposes only and is based on the general classifications provided by the World Health Organization. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. For any health concerns, please consult with a qualified healthcare provider who can assess your individual situation.
Authoritative Source:
Our Commitment to Accuracy: All information on this page regarding BMI classifications and health risks is sourced directly from the “Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Report of a WHO Consultation” (WHO Technical Report Series 894), to provide you with the most reliable and authoritative information possible.
FAQ
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple numerical measure of your weight in relation to your height. It’s a widely used, reliable indicator to determine if you are underweight, in a healthy weight range, overweight, or obese. Knowing your BMI is important as it helps you understand your risk for certain health problems, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
BMI is a very useful tool for most people, but it has some limitations. It may not be accurate for certain groups, such as:
1. Athletes and bodybuilders: Their high muscle mass can result in a higher BMI, even if their body fat is low.
2. Pregnant women: Weight gain is natural during pregnancy, so BMI is not applicable.
3. Children and teenagers: Their BMI must be interpreted using age- and sex-specific percentile charts.
4. The elderly: They may have less muscle mass.
It’s a good starting point, but should not replace a consultation with a healthcare professional.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the standard BMI ranges for adults are:
1. Underweight: Below 18.5
2. Normal (Healthy) Weight: 18.5 to 24.9
3. Overweight: 25.0 to 29.9
4. Obesity: 30.0 and above
The goal for most adults is to maintain a BMI within the 18.5 to 24.9 range.
If your BMI is outside the normal range, it’s a good idea to consult with a doctor or a qualified healthcare provider. They can give you personalized advice. Generally, achieving a healthier BMI involves sustainable lifestyle changes, including:
1. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet.
2. Increasing your level of physical activity.
3. Getting adequate sleep and managing stress.
Remember, this calculator is a tool to provide information, not a medical diagnosis.